VAT in the UAE: How and When it Becomes Applicable?
Get in touch
Recent Posts

Value Added Tax (VAT) in the UAE is a significant part of the country’s tax framework, impacting businesses and consumers alike. Introduced in 2018, VAT is levied on most goods and services, with specific rules for its application. Understanding when VAT becomes applicable is essential for businesses to ensure compliance and avoid penalties. In this blog, we will explore how VAT works in the UAE, when it applies, and the key considerations for businesses navigating this tax system.
What is VAT in the UAE and How Does It Work?
Value Added Tax (VAT) in the UAE is a consumption tax introduced in 2018 at a rate of 5%. It applies to most goods and services and was implemented to reduce reliance on oil revenues.
VAT works by taxing the value added at each stage of production or distribution. Businesses collect VAT on sales and pay VAT on purchases. They can then reclaim the VAT paid on business expenses. The difference between the VAT collected and paid is paid to the government.
For businesses, understanding VAT is essential for compliance and efficient tax management. It affects pricing, operations, and overall costs, making VAT registration necessary for businesses meeting the threshold requirements.
Read Also: Sharjah Free Zone License Guide in 2025
Why Was VAT Introduced in the UAE?
VAT was introduced in the UAE on January 1, 2018, as part of the government’s effort to diversify its revenue sources. Historically, the UAE’s economy relied heavily on oil exports, but with fluctuating oil prices, the country sought to reduce its dependency on this sector.
The introduction of VAT aimed to create a sustainable revenue stream, helping the government fund infrastructure, public services, and social welfare programs. It also aligned the UAE with global tax practices, improving its position in international trade.
By implementing VAT, the UAE can continue investing in its economy, reducing the pressure on oil revenues, and ensuring long-term economic stability.
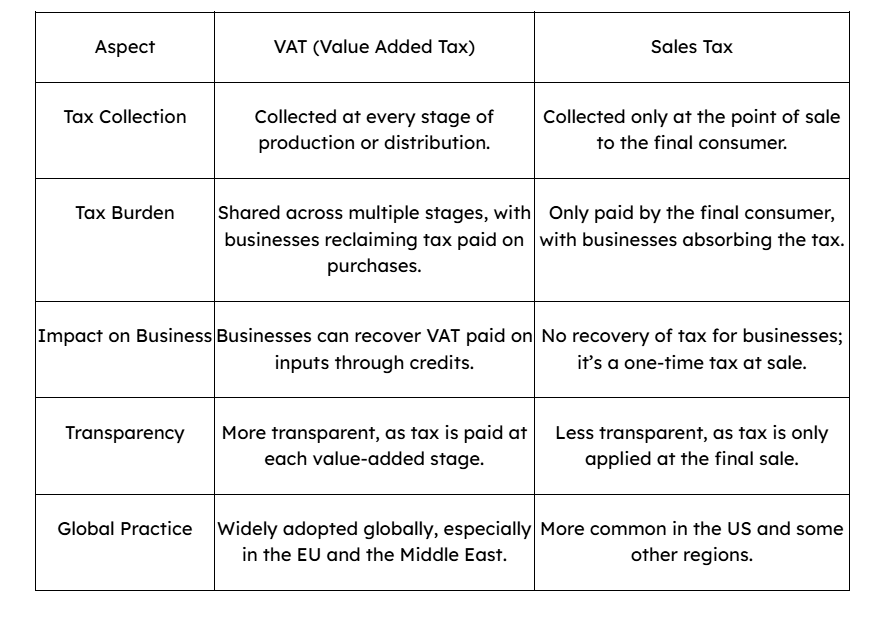
VAT vs Sales Tax: Key Differences Explained
While both VAT and sales tax are consumption taxes, they differ in how they are applied. Understanding these differences helps businesses navigate tax obligations more effectively.
Types of VAT in the UAE
In the UAE, VAT is applied in various ways, depending on the nature of the transaction and the goods or services being provided. The VAT system ensures that different categories of transactions are treated appropriately, reflecting the nature of the goods or services involved.
Here are the main types of VAT applied in the UAE:
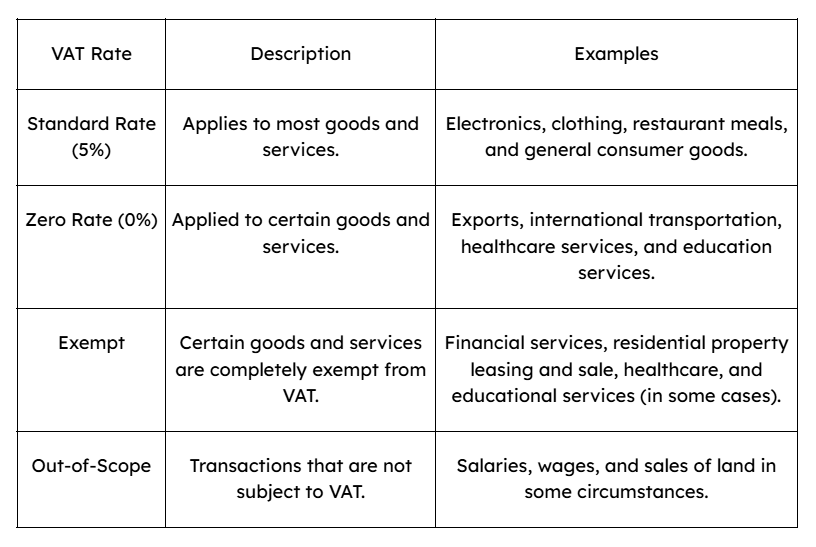
1. Standard Rate VAT (5%)
The standard VAT rate in the UAE is 5%. This rate applies to most goods and services unless explicitly exempted or zero-rated. Businesses that deal in taxable goods and services are required to charge VAT at this rate on the sale of their products or services. They must also pay VAT on purchases, which can be claimed back if they are VAT-registered.
2. Zero-Rated VAT (0%)
Certain goods and services in the UAE are subject to zero-rated VAT. This means that VAT is charged at 0%, but businesses can still reclaim VAT on their input costs. Common zero-rated items include:
- Exports of goods and services outside the UAE
- International transportation services (e.g., air travel)
- Some healthcare services
- Educational services
- Residential real estate sales (subject to conditions)
The zero-rated system benefits businesses in these sectors because they can recover the VAT paid on business expenses, making it cost-neutral for them.
3. Exempt VAT
Some goods and services are completely exempt from VAT. This means VAT is not charged, and businesses cannot reclaim VAT on related purchases. The exemptions typically apply to:
- Certain healthcare services (e.g., medical services provided by government institutions)
- Financial services (e.g., insurance and banking services)
- Residential property leasing and sales (in some cases)
Exempt goods and services do not allow businesses to claim VAT refunds on inputs, making it important for businesses in these sectors to understand their obligations.
4. Out-of-Scope Transactions
These are transactions that fall outside the scope of VAT in the UAE. They are neither taxable nor exempt, and no VAT is applied to them. Examples include:
- Salaries and wages paid to employees
- The sale of land (subject to the specific regulations on real estate)
- Certain transactions between government bodies
Although these transactions do not attract VAT, businesses must still keep accurate records for reporting purposes and ensure they are not mistakenly charged VAT for them.
5. Special VAT Schemes
In addition to the standard VAT rates and exemptions, the UAE also has specific VAT schemes designed to cater to particular industries or circumstances, such as:
- VAT for Small Businesses: Small businesses with taxable supplies less than AED 187,500 may opt for voluntary VAT registration, allowing them to comply with VAT laws while enjoying certain exemptions.
- Tourism and Hospitality VAT: Special VAT rates or exemptions apply to the tourism sector, covering hotel accommodations and related services.
These special schemes help businesses adapt to the complexities of VAT in the UAE and manage their tax liabilities efficiently.
Also Read: Check UAE Visa Status: A Complete Guide to Tracking and Cancelling Your Visa
How to Register for VAT in the UAE
Registering for VAT in the UAE is a crucial step for businesses whose taxable supplies exceed the mandatory threshold. The registration process ensures that businesses comply with the VAT laws and can properly collect and pay VAT to the government. Here’s a guide on how to register for VAT in the UAE:
1. Determine Whether VAT Registration is Required
Before registering, businesses must determine if they meet the mandatory VAT registration threshold. As of 2025, businesses must register for VAT if their taxable supplies exceed AED 375,000 annually. If a business’s turnover is below this threshold, VAT registration is voluntary but can be beneficial for claiming input VAT credits.
2. Prepare Required Documents
To register for VAT, businesses must provide the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) with several key documents. These typically include:
- A valid trade license or commercial registration
- Proof of the company’s legal status (e.g., the company’s Articles of Association)
- Details of the business activities and revenue projections
- Bank account details
- Emirates ID or passport copies of the owners or authorized signatories
- Copies of contracts or invoices, if applicable
3. Create an Account on the FTA Portal
Businesses must create an account on the Federal Tax Authority’s online portal (https://tax.gov.ae) to initiate the VAT registration process. This portal is where you will submit the application and track its status. You’ll need a valid email address and contact details to register on the portal.
4. Complete the VAT Registration Form
Once the account is created, businesses can fill out the VAT registration form on the FTA portal. The form requires businesses to provide:
- Company name, address, and contact information
- Type of business activity
- Expected turnover and details of taxable supplies
- Tax representative details (if applicable)
- VAT-related bank account details
It’s important to provide accurate and complete information to avoid delays or rejection of the application.
5. Submit the Application
After completing the registration form, submit it online through the FTA portal. Ensure that all required supporting documents are attached. The FTA may review the application and request further clarification if necessary.
6. Wait for Approval
The FTA will process the VAT registration application, which typically takes up to 20 business days. During this period, they may contact the business for additional information or clarification. If the application is approved, the business will receive a VAT registration number.
7. Receive VAT Registration Number
Once approved, the business will be issued a VAT registration number. This number must be used on all invoices and VAT-related documents. Businesses are also required to file regular VAT returns, as per the requirements of the FTA.
8. Comply with VAT Filing Requirements
After registration, businesses are required to file VAT returns on a quarterly or annual basis, depending on their turnover. Regular filings must include details of the VAT collected on sales and the VAT paid on purchases. Businesses must also make VAT payments to the FTA by the due date to avoid penalties.
9. Optional VAT Deregistration
If a business’s taxable supplies fall below the VAT registration threshold (AED 375,000) for the past 12 months, it may apply for voluntary deregistration. The process involves submitting an application to the FTA and providing proof of falling below the threshold.
By following these steps, businesses can efficiently register for VAT in the UAE and ensure compliance with local tax laws. Proper registration allows businesses to reclaim VAT on their inputs and avoid any legal penalties.
VAT Rates in the UAE
The UAE has implemented a 5% VAT rate for most goods and services, making it one of the lowest VAT rates globally. However, certain goods and services are subject to either zero-rating or exemptions depending on the nature of the transaction.
Here is a breakdown of the VAT rates applied in the UAE:
Impact of VAT on Individuals and Businesses in the UAE
The introduction of VAT in the UAE has had significant implications for both individuals and businesses. While it offers a stable source of revenue for the government, it also affects the cost of goods and services, tax compliance, and overall business operations.
Impact on Businesses
- Increased Administrative Burden
Businesses are now required to register for VAT if their taxable turnover exceeds the threshold of AED 375,000. This means maintaining accurate records, issuing VAT-compliant invoices, and submitting regular VAT returns. The administrative effort may require additional staff or software to manage the tax process effectively.
- Impact on Cash Flow
Businesses collect VAT on their sales and pay VAT on their purchases. This can impact cash flow, especially if a company has to wait for VAT refunds from the government. Managing VAT payables and receivables is essential to avoid liquidity issues.
- VAT on Input Costs
Many businesses can reclaim VAT paid on business-related purchases. This helps offset the tax burden. However, businesses in sectors that deal with exempt or zero-rated goods may not be able to recover VAT on their inputs, potentially increasing their costs.
- Price Adjustments
As VAT is passed on to consumers, businesses may adjust their pricing to reflect the tax, which could make products or services more expensive. This can influence consumer behavior and demand, especially for price-sensitive goods.
Impact on Individuals
- Higher Living Costs
As VAT applies to most goods and services, individuals may experience higher living costs. Common goods such as groceries, electronics, and dining out will incur a VAT charge, affecting household budgets.
- Increased Awareness of Consumption
With the introduction of VAT, individuals may become more mindful of their spending, especially when they see VAT added to prices at the checkout. VAT may also encourage people to consider cheaper alternatives or buy in bulk to save on taxes.
- Exemptions on Basic Necessities
To mitigate the impact on lower-income households, certain essentials such as healthcare, education, and basic food items are either zero-rated or exempt from VAT. This helps ensure that basic living standards are not heavily impacted by the tax.
What are the VAT Exemptions in the UAE
The UAE VAT system provides exemptions to ease the tax burden on essential services and goods. Here’s an enhanced overview of the key VAT exemptions:
1. Healthcare Services
Healthcare services, including treatments, doctor consultations, medical supplies, and health insurance, are exempt from VAT, ensuring affordable access to healthcare for all.
2. Educational Services
Education-related services, such as school fees, university tuition, vocational training, and educational materials (e.g., textbooks), are exempt to ensure that education remains accessible.
3. Residential Properties
The sale and leasing of residential properties are VAT-exempt, meaning individuals do not pay VAT on residential property transactions, though commercial properties are taxable.
4. Financial Services
Essential financial services such as loans, mortgages, insurance, and currency exchange are exempt from VAT, supporting the smooth functioning of the financial sector.
5. Exports of Goods and Services
Exports outside the UAE are zero-rated, meaning VAT is not charged, making UAE goods and services more competitive in global markets.
6. Public Transport
Public transport services, including buses, metro, and train systems, are exempt from VAT, ensuring that public transportation remains affordable and accessible to residents and tourists alike.
7. Cultural and Social Services
Cultural institutions like museums, art galleries, and public events (sponsored by the government) are exempt from VAT, promoting cultural growth and public access.
8. Charitable and Non-Profit Organizations
Services provided by registered charitable and non-profit organizations, including donations and community-based services, are exempt from VAT and support social welfare.
What are the Penalties for Non-Payment of VAT in the UAE
Failing to pay VAT on time in the UAE can lead to significant financial penalties. The Federal Tax Authority (FTA) enforces a structured penalty system to encourage timely compliance.
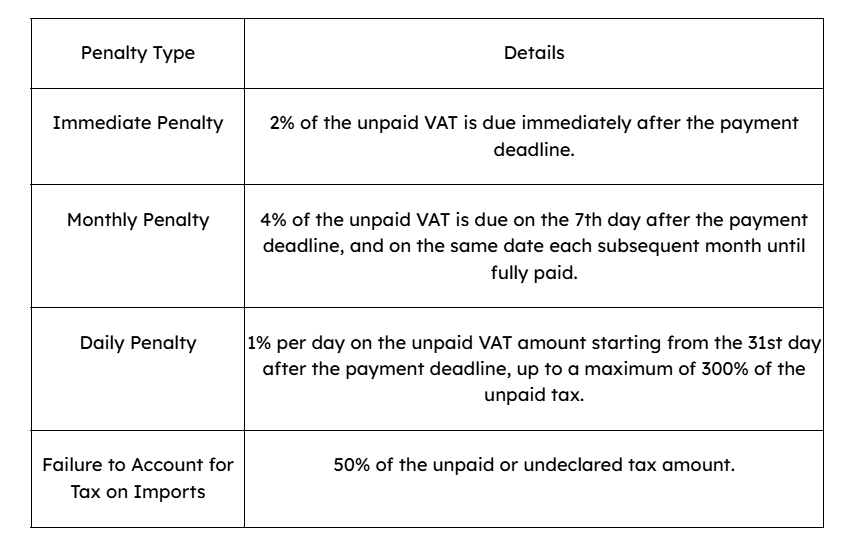
These penalties are designed to ensure timely payment and accurate reporting of VAT obligations. Businesses should maintain proper records and adhere to filing deadlines to avoid these substantial fines.
How SetupMate Can Assist with VAT in the UAE
SetupMate offers expert guidance to businesses navigating VAT regulations in the UAE. From VAT registration to compliance and filing, our team ensures your business meets all VAT requirements seamlessly. We provide personalized solutions, helping you avoid penalties and optimize your tax processes. Whether you’re a new business or expanding, we simplify VAT management so you can focus on growth.
Are you looking to start your business in Dubai? Check out our blog on SIRA approval in Dubai for more insights on setting up securely and smoothly.


